
As banks continue to evolve their funding strategies, a notable shift is reshaping how financial institutions approach them. Reciprocal deposits, once a niche tool, have surged to the forefront of core deposit management, particularly for community banks seeking stable and flexible funding sources.
A Dramatic Surge in Adoption
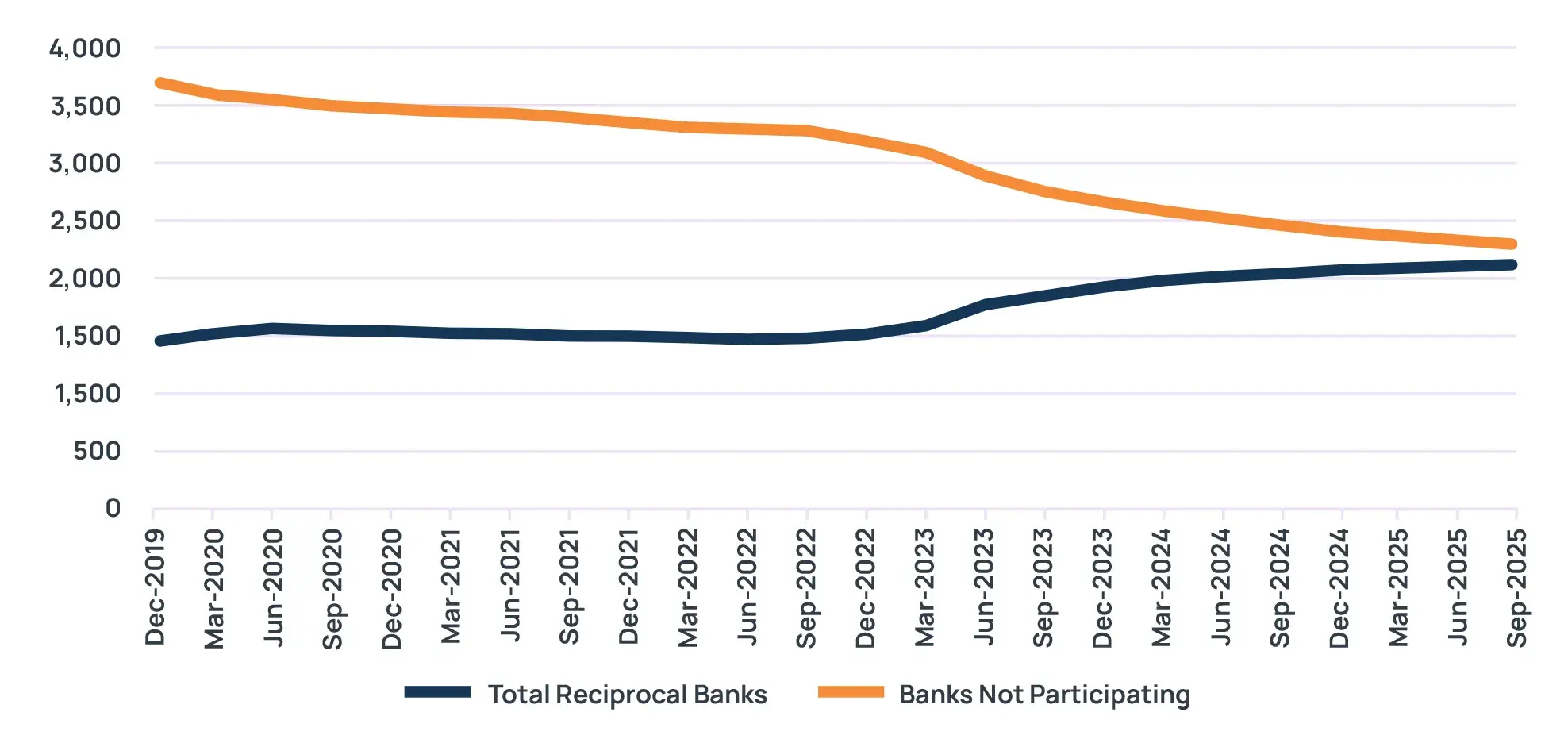
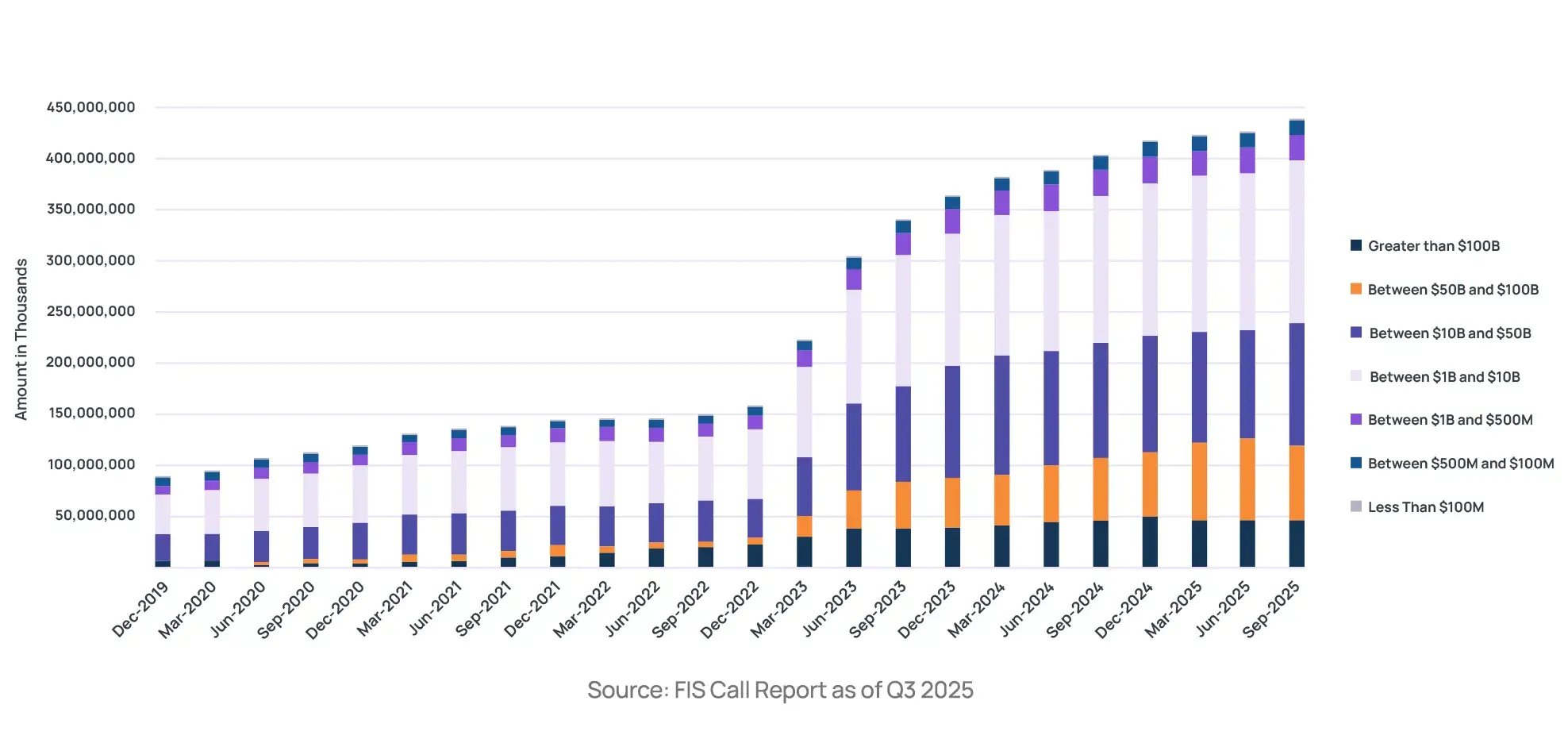
The numbers tell a compelling story. Total reciprocal deposits have nearly tripled, skyrocketing from approximately $156 billion in December 2022 to an impressive $440 billion by September 2025 (based on FFIEC call reports). The number of participating banks also climbed from around 1,523 to 2,105 over this period. This remarkable growth underscores the intensifying competition for core deposits and the industry’s drive for reliable funding alternatives.
The Changing Face of Core Deposits
Community banks and other small financial institutions can leverage the power of reciprocal deposits to even the playing field with the larger banks. These community banks face intense competition from larger institutions and constant pressure to manage overhead costs, while mitigating deposit flight risks. Reciprocal deposits present a solution, giving community banks the ability to offer access to expanded FDIC-insurance on funds in order to capture large balance accounts, providing a strategic advantage in a crowded market.
Why Reciprocal Deposits Are Gaining Ground

Regulatory Recognition and Investor Confidence
More explicit regulatory guidelines have paved the way for broader acceptance of reciprocal deposits. The industry witnessed significant growth spikes, with two consecutive quarters in early 2023, each seeing approximately 42% jumps in adoption rates. Subsequent quarters continued to show steady rises, cementing reciprocal deposits as a mainstream funding strategy. This shift is also evident in the decreasing number of non-participating banks, which fell from 3,201 to 2,274 during the same period.
Flexibility for Growth
Reciprocal deposits empower banks to give their customers access to expanded FDIC deposit insurance coverage on large deposits by splitting funds among multiple receiving institutions. As a result, banks maintain larger, more stable balances in their portfolios, fueling greater liquidity and lending capacity.
Industry Adoption Trends
The adoption of reciprocal deposits has been widespread but particularly notable among specific bank sizes:
-
Smaller banks with less than $1 billion in assets have shown the fastest adoption, increasing to 1,271 participating institutions (up from approximately 1,063 in Dec 2022). They now hold $40.0 billion in reciprocal balances.
-
Banks with assets between $1 billion and $10 billion continue to hold the largest share of reciprocal balances, totaling $161.5 billion across 719 banks (up from roughly 564 banks holding $69.7 billion in Dec 2022).
-
Institutions with assets between $10 billion and $50 billion now account for $118.8 billion in reciprocal deposits across 84 banks, reflecting an increase in total balances despite a slight decrease in the number of participating institutions.
Case Study: Expanding Deposit Base
Consider a mid-sized community bank aiming to expand its commercial lending book. The bank embraced reciprocal deposits because high-balance depositors often choose larger institutions for perceived safety. By offering depositors access to expanded FDIC deposit insurance coverage while keeping the relationship in-house, the bank attracted more substantial accounts and addressed deposit insurance concerns. It secured a more stable funding base to support its expanding lending activities.

Conclusion: A New Standard in Deposit Strategy
The steady rise in both volume and participation in reciprocal deposits signals more than a passing trend—it’s becoming the new standard in deposit strategy. For community banks, reciprocal deposits offer a powerful tool for effectively competing with larger banks, managing risk, and fostering growth.